- Original Article
- COPD
- Factors Associated with the Discrepancy between Exercise Capacity and Airflow Limitation in Patients with Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease
- Tae Hoon Kim, I Re Heo, Na Young Kim, et al.
- Tuberc Respir Dis. 2024;87(2):155-164. Published online January 16, 2024
-

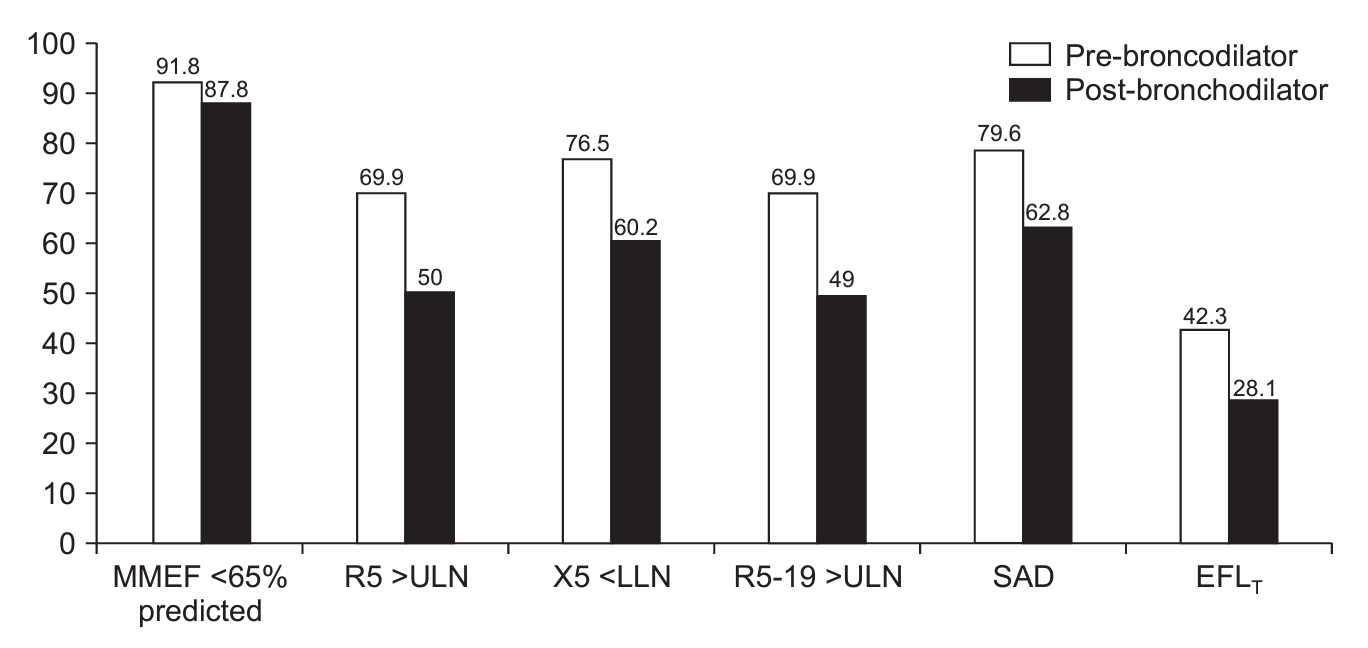
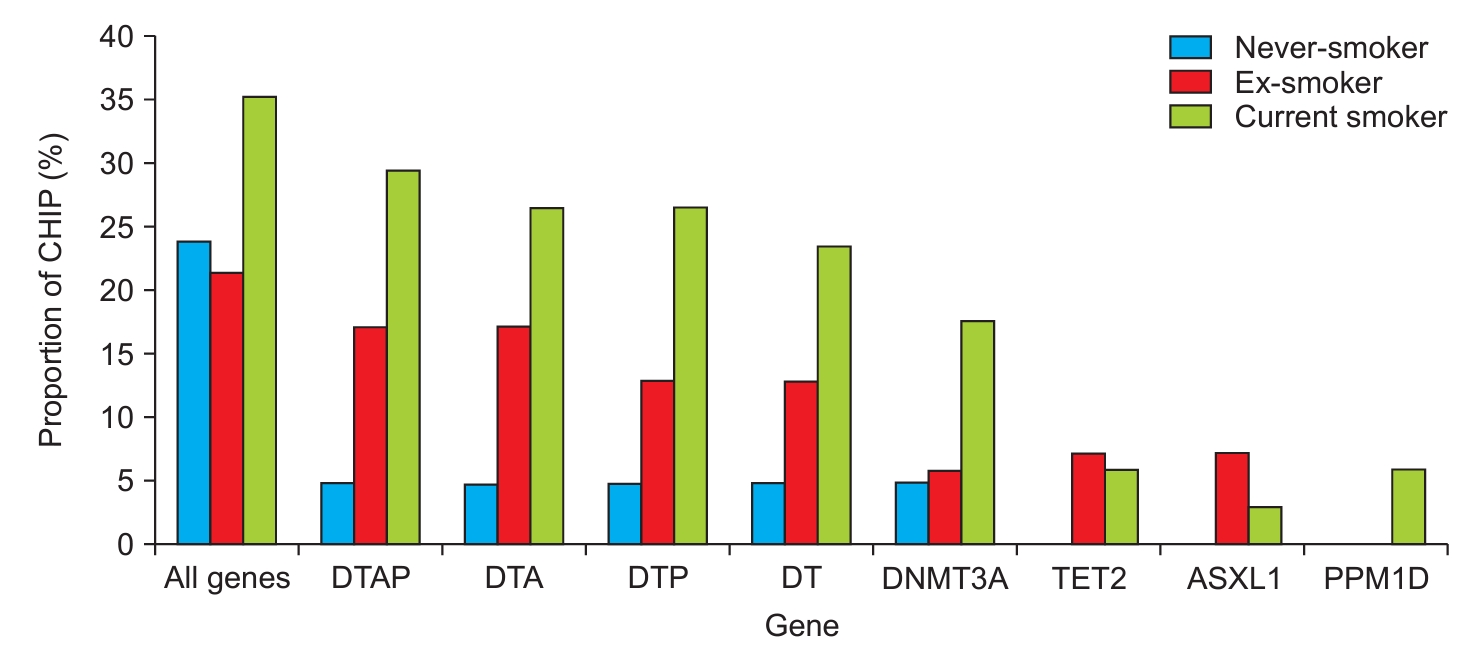
Background: Exercise capacity is associated with lung function decline in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) patients, but a discrepancy between exercise capacity and airflow limitation exists. This study aimed to explore factors contributing to this discrepancy in COPD patients. Methods: Data for this prospective study were obtained from the Korean COPD Subgroup Study. The exercise capacity and airflow limitation were assessed using the 6-minute walk distance...